A recently published peer-reviewed scientific article “Cannabinol Modulates Neuroprotection and Intraocular Pressure: A Potential Multi-Target Therapeutic Intervention for Glaucoma” has provided insight into unique therapeutic potential of Cannabinol (CBN) for glaucoma treatment
The article, published in a leading international journal Biochimica et Biophysical Acta (BBA – Molecular Basis of Disease) (LINK to the article) highlights research* results from several studies that evaluated the survival of retinal ganglion cells, modulation of intraocular pressure and its effects on extracellular matrix proteins using in vitro and in vivo glaucoma models.
The research provides two key findings:
- CBN may promote neuroprotection of cells in the retina that are responsible for vision,
- CBN may normalize intraocular pressure (that causes damage in cases of glaucoma) by attenuating changes in the extracellular matrix proteins
The article also reports on the comparison of CBN with other cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), with results indicating that CBN has a stronger effect and broader neuroprotective therapeutic range.
This research has significant implications for neuroprotection and may lead to a potential new treatment for millions of people worldwide who are suffering from this condition that damages nerves in the eye and can lead to vision loss and blindness.
What is Cannabinol (CBN)?
Minor cannabinoid, found in trace amounts in the Cannabis plant. CBN is one of the more than 100 cannabinoid compounds present in the Cannabis plant at very low levels. In total, all minor (aka rare) cannabinoids are estimated to make up less than 1% of the Cannabis plant.
It is produced from the degradation of THC. CBN occurs naturally as a degradant of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). As the plant dries and THC is exposed to air, light and heat, CBN is produced in trace amounts.
With a unique chemical structure different from other cannabinoids. CBN has distinct affinity and specificity for receptors in the human body, including those in the endocannabinoid system, that result in different biological effects in humans. As opposed to THC, CBN is generally accepted as non-psychoactive.
How does Cannabinol (CBN) work in the human body?
Scientific literature suggests that Cannabinol (CBN) interacts with endocannabinoid receptors in the human body and modulates them.
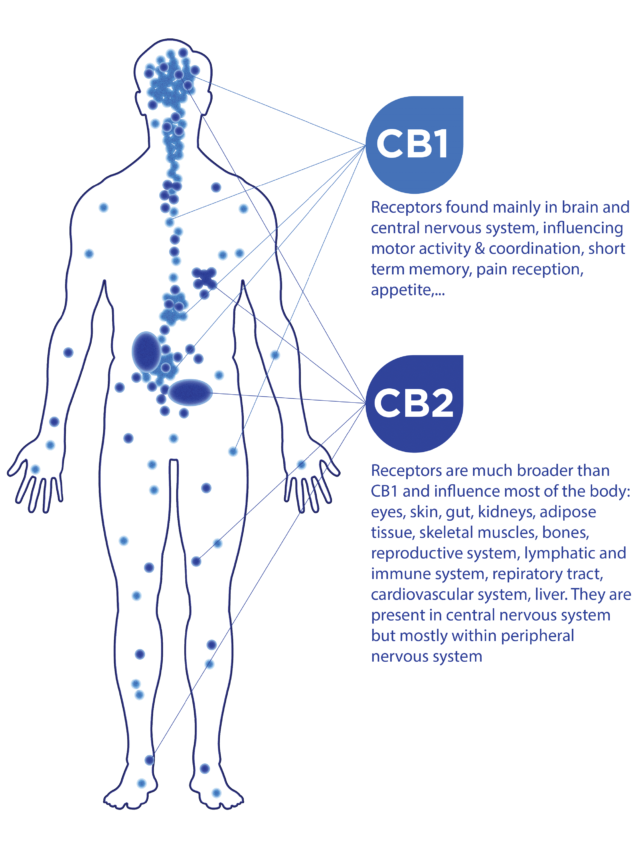
Endocannabinoid receptors are present throughout the body. They are components of the Endocannabinoid System; a system that is involved in a variety of physiological processes including pain, mood, memory, immune function, sleep and appetite. Endocannabinoid receptors are activated by endocannabinoids or exogenous agonists such as CBG, CBN, THC.
There are two main types of receptors that make up the main part of the human endocannabinoid system: CB1 and CB2.
The Cannabinol (CBN) seems to be particularly affecting the cannabinoid receptors type 2 (CB2) that are identified in peripheral tissues and cells associated with the immune system. New findings suggest that the activation of CB2 receptors may be the key to the treatment of peripheral nervous system disorders, incl. glaucoma. It is beneficial that CB2 is devoid of central side effects.
References:
Bie B, Wu J, Foss JF, Naguib M. An overview of the cannabinoid type 2 receptor system and its therapeutic potential. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2018;31(4):407-414.
Cabañero D, Martín-García E, Maldonado R. The CB2 cannabinoid receptor as a therapeutic target in the central nervous system. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2021 Aug;25(8):659-676.
De Laurentiis A, Araujo HA, Rettori V. Role of the endocannabinoid system in the neuroendocrine responses to inflammation. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(29):4697-706.
Finn, David P.a,*; Haroutounian, Simonb; Hohmann, Andrea G.c; Krane, Elliotd; Soliman, Nadiae; Rice, Andrew S.C.e Cannabinoids, the endocannabinoid system, and pain: a review of preclinical studies, PAIN: July 2021 – Volume 162 – Issue – p S5-S25.
Somvanshi RK, Zou S, Kadhim S, Padania S, Hsu E, Kumar U. Cannabinol modulates neuroprotection and intraocular pressure: A potential multi-target therapeutic intervention for glaucoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022 Mar 1;1868(3):166325. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166325. Epub 2021 Dec 16. PMID: 34921975.
*Collaborative research was done between the University of British Columbia and InMed Pharmaceuticals, a Vancouver-based company that has developed CBN eyedrops as a potential treatment for glaucoma.


